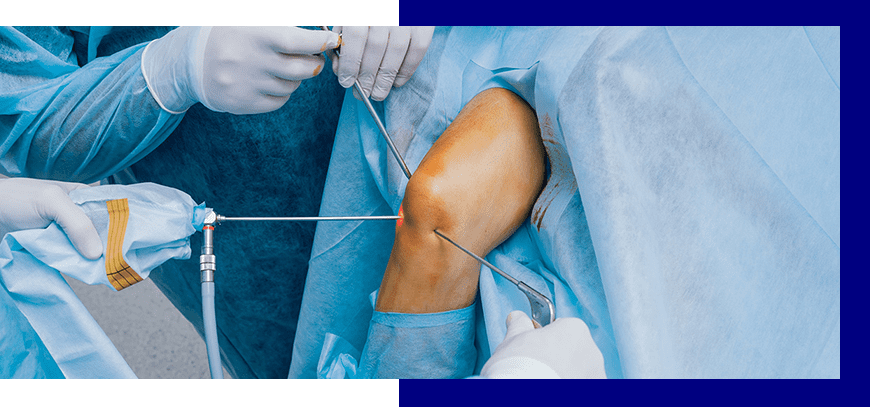
Knee Arthroscopy is performed for a variety of conditions, most commonly being:
- Meniscal tears
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tear
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) tear
- Synovitis like Rheumatoid Arthritis, PVNS etc
- Loose bodies
- Patellar subluxation or dislocation
- Cartilage Damage
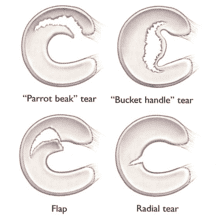
Meniscus Tear
The meniscus is a fibrocartilagenous disc in the knee joint which when torn is known as a meniscal tear. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting or more commonly by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear' called a degenerative tear. Tears can lead to pain and/or swelling of the knee joint. Sometimes Patients may also feel clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the knee joint.
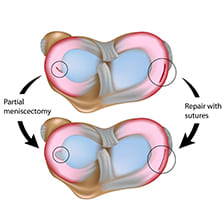
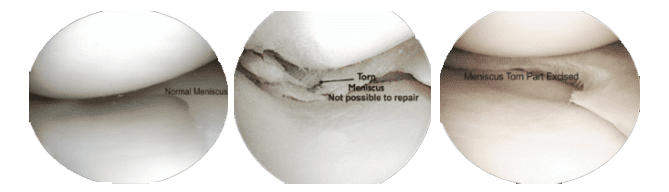
The tear can be diagnosed clinically and confirmed by an MRI Scan of the knee. Initial treatment is rest, ice application, compression and elevation. Symptomatic tears may require arthroscopic surgery for removal of torn part of meniscus (Partial Meniscectomy) while some particular tears can also be repaired.
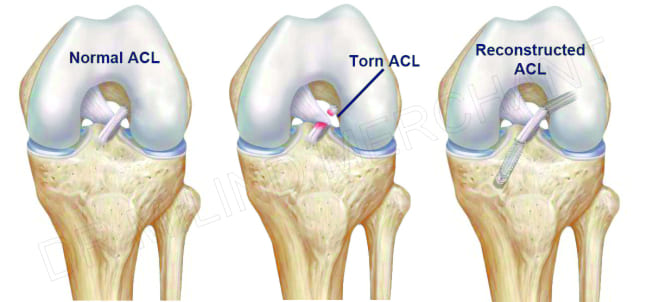
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury
The ACL is one of the most important ligaments giving the Front-to-back and Rotational Stability to the knee.
Most common cause for its injury is twisting injury to the knee which may occur while playing sports, dancing or even getting down from a bus or train.
Patients with a torn ACL feel swelling in the knee, a feeling of instability or "looseness" or "feeling of giving way" in the knee along with pain in the knee. ACL tears may be associated with cartilage damage or meniscal tears.
Diagnosis is made by clinical examination and MRI.
Patients with symptomatic tear require Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction usually done by using Hamstring tendons from the same knee.
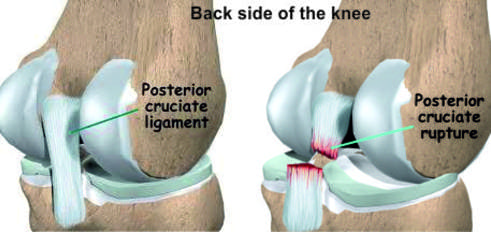
Posterior cruciate ligament (or PCL) Injury
It is a strong ligament in the back of the knee contributing to Front-to-back stability along with ACL.
Common causes of PCL injuries are direct blows to the flexed knee, such as the knee hitting the dashboard in a car accident or falling hard on the knee.
Symptoms patients may have are a feeling of instability in the knee and pain in the knee.
Treatment consists of Physiotherapy and Bracing failing which Arthroscopic Surgery may be needed.
Cartilage Injuries
Cartilage is the coating covering the joint surfaces making the joint motion smooth. It can be injured during a knee injury along with a ligament or meniscus injury or alone. Damage to cartilage may also be seen in osteoarthritis of the knee where its tear has occured due to wear and tear changes.
Diagnosis of a cartilage injury can be usually made by MRI scans and may also be seen while during arthroscopy of the knee.
Treatment of such a cartilage injury depends on the size of tear, the site and the depth of injury.
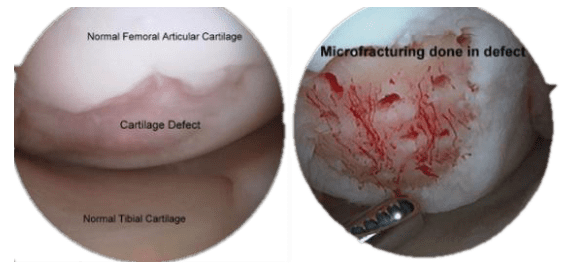
Various Cartilage procedures done are divided into Reparative and Restorative procedures
- Reparative Procedures are Drilling of cartilage (done to improve blood supply to cartilage) and Cartilage Fixation which can be done for Osteochondritis dessicans (OCD) or Osteochondral Fractures.
- Restorative Procedures include microfracture of the catilage bony bed, Osteochondral Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation (OATS) and Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI).
Recovery: Cartilage injuries usually need longer periods of protected weight bearing of the involved leg for the injuries to heal.
 +91-99304 10318
+91-99304 10318